What do we mean by electromagnetic (EM) waves?
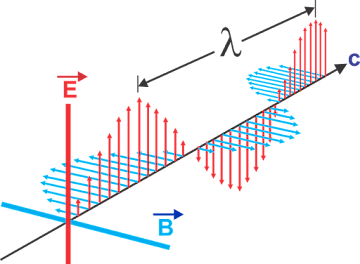
The electromagnetic waves (also known as EM waves) are formed as a result of the vibrations between the electric field and magnetic field.In simple words, these are the waves of the electromagnetic field which make up a family of waves known as the electromagnetic spectrum.
The EM waves, such as radio, micro, ultraviolet and X-rays, propagate through space carrying electromagnetic radiant energy.
Let me further explain this with the help of an example. The light from a lamp in your house is a type of electromagnetic radiation. Similarly, the waves travelling from the radio station are also a type of electromagnetic radiation.
In the electromagnetic spectrum (refers to the range of frequencies of the electromagnetic radiations in order with their respective wavelengths), the EM waves are arranged in order of their frequencies and wavelengths.
Radio wave (which have the longest wavelength and the lowest frequency) is the first in the electromagnetic spectrum while gamma rays (which have the shortest wavelength and highest frequency) are the last.
Note: Gamma rays have the highest energy in the electromagnetic waves because they have the greatest frequency.
The EM waves are mentioned below in respect to their frequencies and wavelengths.
- Radio waves (greatest wavelength, lowest frequency)
- Microwaves
- Infrared
- Visible light
- Ultraviolet
- X-rays
- Gamma rays (greatest frequency, lowest wavelength)
You can use the following mnemonic (a pattern of words which assists in learning something) to learn the order of these waves:
Red Monkeys In Vans Use X-ray Guns
This takes us to another very important topic which is about the properties of electromagnetic waves, so let's discuss that topic in detail now.
Properties of EM waves:
- They carry no electric charge
This is because the EM waves are neutral in nature.
- They do not require a medium to propagate
This means that these waves travel through the vacuum because they are very powerful.
- EM waves are transverse waves (waves that vibrate perpendicularly to the path of propagation)
This is because the magnetic and electric field oscillate at 90° to each other.
- They travel at the same speed of 3x10^8 m/s (speed of light) in a vacuum and transfer energy from one place to another
- Electromagnetic waves obey the laws of reflection and refraction
- When EM waves move from one medium to the other (for example from glass to air), their speed and wavelength change
However, their frequency remains unchanged in all mediums.
You should also know that mathematically, we can calculate the speed of the EM waves with the help of a formula.
The formula says:
v = f x λ (where v = wave speed, f = frequency of the wave and λ = wavelength of the wave).
Visible spectrum:
Colour is a quality of light and light has properties in common with particles and waves.
Moreover, the beans of light have different values of frequency (number of waves passing through a fixed point in one second) and wavelength.
You should know that in the colour spectrum, red has the smallest frequency and the longest wavelength while violet has the highest frequency and the shortest wavelength.
- Red (shortest frequency, longest wavelength)
- Orange
- Yellow
- Green
- Blue
- Indigo
- Violet (longest frequency, shortest wavelength).
You should also know about the application of electromagnetic waves in practical life. So, let's discuss the topic.
Application of electromagnetic waves:
Radio Waves:
They are used in the standard broadcast radio, air-traffic control, television, remote-controlled toys and for navigation as well.
Since radio waves have the longest wavelength, they can travel over obstacles, such as mountains). Different frequencies of radio have variable propagation characteristics.
They can produce high voltage AC transmission lines and can transmit power over long distances.
The radio waves with longer wavelength are also used for submarine communication and waves with shorter wavelength are used as FM (frequency modulation) radio.
Ultraviolet rays:
Ultraviolet radiations are used in medical, dental and industrial processes for multiple purposes such as killing bacteria, curing resins and inks and suntanning.
You can also say that UV (ultraviolet) radiations are used in sunbeds for tanning. This use is controversial because constant exposure to UV rays can lead to skin cancer.
UV rays have the ability to inactivate viruses and bacteria and therefore, they are used for sterilizing equipment (medical and laboratory).
Furthermore, these rays are also used in "curing". One example is the hardening of glues by this process.
Microwaves:
Microwaves are extensively used in modern technology.
For instance, they are used in wireless networks, spacecraft communication, radar satellite and for cancer treatment as well.
Moreover, these waves are also used in microwave ovens as a source of transferring energy. They heat the food by penetrating into it and as a result, water molecules vibrate vigorously to produce heat.
Mobile phones, speed cameras, aircraft, ships and weather forecasters also use microwaves.
Microwaves are also used in carrying signals to and from satellites for the global positioning system (GPS). This is because they can penetrate through the atmosphere and pass light, haze, snow and rain as well.
There are plenty of other uses of microwaves as well but some of the prominent ones are mentioned above.
Visible light:
We use visible light images to predict the weather by watching clouds. In short, visible light has multiple uses in terms of "sight".
Apart, visible light is also used for making lasers for multiple purposes such as for surgery. These waves also make our television, mobile phone screens and computer.
Visible light is also used in optical fibres for telecommunications and medical purposes.
Infrared radiation:
These waves are used in detecting heat loss in insulated systems, detecting overheating of electrical apparatus and are also utilised for studying blood flow in the skin.
In terms of military, these are used for surveillance, tracking homing and target acquisition.
Apart, the infrared remote controllers are utilised for controlling multiple electrical devices such as television and air conditioner. The temperature of the human body can also be detected by measuring the number of infrared radiations emitted by our body.
These waves are also used by electrical heaters, cookers, optic fibres and thermal imaging cameras (to detect people in the dark) but these radiations can cause burns to the skin.
X-rays:
X-rays are the high-frequency (and can penetrate through the human body) waves and are used to kill cancer cells in radiation therapy.
They are also used to detect and diagnose a bone fracture, infections, some tumours, dental issues and bone loss as well.
In terms of security, they play an important part in detecting equipment in the bags and are also used to check tiny flaws in heavy metal equipment.
X-rays are also used in detecting digestive problems, blood vessels blockage and heart problems such as congestive heart failure.
Gamma rays:
Gamma rays are used in medicine (radiotherapy) and industry (sterilization and disinfection).
They have high penetration power and therefore, they are used for treating brain tumours to kill cancer cells.
Gamma rays are also used in detecting minerals underground and they can bring about significant biochemical changes in the living cells (making them suitable for radiation therapies).
Therefore, exposure to these ionizing radiations can cause cancer.
These are some of the application of the electromagnetic waves which you should be familiar with.
Conclusion:
With this, the article about electromagnetic waves has come to an end. I hope that all your queries have been answered.
The topics covered in this article are listed below for your reference.
- Electromagnetic waves
- Visible spectrum
- Application of electromagnetic waves
Thank you very much for reading.



Comments
Post a Comment