Homeostasis is a very important topic in biology (5090) and there are multiple concepts in this topic which you need to learn.
First of all, you should know that what is meant by homeostasis?
The system of a body which is responsible for the maintenance of the internal environment is known as homeostasis.
In other words, it is the ability to maintain a stable state that continues despite the changes outside. This system ensures the survival of all species from plants to animals.
This was all about the introduction of this topic. Now, let's move into further details and learn about some other topic as well.
Negative feedback:
To maintain a constant internal environment, a significant principle known as negative feedback occurs. In other words, it is the principle on which homeostasis works.
In biological systems, negative feedback (a regulatory mechanism) is a type of regulation that occurs when a specific stimulus (change) is detected.
For instance, when the temperature of your body will rise, the body will bring about specific actions in order to reduce the temperature. This opposite change is known as negative feedback.
Some of the examples of negative feedback are listed below:
- Thermoregulation (a mechanism to restore the body temperature when it changes).
- The maintenance of blood glucose level (insulin to reduce it and glucagon to increase the glucose level).
- Osmoregulation (to retain the water potential of the body).
We will discuss all these examples in detail in this article.
Now you might be wondering, how does negative feedback occur? Let me tell you.
Firstly, any change (stimulus) occurs. Secondly, the receptor in the body detects this change. When the change is detected, a mechanism to correct that change occurs.
In this way, negative feedback (an opposite effect to the change) occurs.
Examples of homeostasis:
Osmoregulation:
Osmoregulation refers to the mechanism in the body that maintains the water potential. The body brings about the opposite change to the stimulus to restore the normal condition.
When the water potential increases (than normal), less ADH (anti-diuretic hormone) is secreted so that less water is absorbed by the body.
Moreover, more water is excreted through the urine and the kidney also absorbs less water.
These opposite changes lower the water potential and as a result, the water potential is restored back to normal. In short, when the water potential rises, the body will reduce the water potential to restore normal conditions.
However, when the water potential in the body decreases, more ADH is secreted so that more water is absorbed by the body and kidneys.
Similarly, less urine is produced to secrete less water and the urine becomes concentrated (because it contains less water). The negative feedback increases the water potential.
As a result, a normal condition is brought about. This is how the water potential of a body is regulated.
Now, you should also know how the glucose level of your body is maintained. So, let's discuss the topic in detail now.
Regulation of blood glucose concentration:
In order to maintain normal glucose concentration in the blood plasma, our body is responsible for certain actions depending upon the concentration of glucose.
For example, when the glucose concentration increases after a meal, the pancreases detect the stimulus (because they act as a receptor) in this case.
Therefore, the pancreas secretes insulin in the bloodstream to decrease blood glucose concentration.
Insulin enters the liver where it converts glucose to glycogen to be stored in the liver. In this way, the glucose concentration is reduced so that normal conditions prevail.
Further reading:
However, when the glucose concentration decreases, pancreases (acting as a receptor) releases glucagon which enters the liver through the bloodstream.
Glucagon converts the stored glycogen to glucose which enters the bloodstream to increase glucose concentration back to normal. This is how negative feedback maintains the glucose concentration in our body.
When the body is unable to maintain the blood glucose concentration, a disease known as diabetes occurs. In type 1 diabetes, the insulin-secreting cells are unable to produce insulin.
As a result, the glucose concentration in the body remains high and the presence of glucose in urine indicates diabetes because the urine of a healthy person will never contain glucose.
This can be treated by injecting insulin which converts glucose to glycogen in the body which is stored in the liver. Some of the symptoms of glucose are:
- Blurred vision
- Weakness or tiredness
- Extreme thirst
- Weight loss
- Loss of consciousness
The people with type 1 diabetes can perform regular exercise to maintain their glucose concentration because glucose level is reduced during exercise as it is used for respiration.
These were some key concepts which you should know about the maintenance of glucose concentration in your body.
Skin and thermoregulation:
Skin is the largest organ of the body and it helps us to maintain the body temperature, protect us from microbes and elements and permits us to feel sensations like hot and cold.
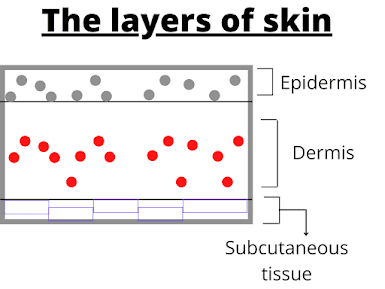
The skin has multiple layers such as:
- Epidermis
- Dermis
- Subcutaneous fat
The epidermis is the part of the skin you see (the top layer of the skin). The epidermis consists of a cornified layer (which prevents germs from entering the body), a granular layer (containing living cells) and a Malpighian layer (which provides skin with its colour).
The dermis is another thick layer, underneath the epidermis, and it has hair follicles (from where the hairs emerge) which cause goosebumps to occur.
During cold, the erector muscles contract causing the hairs to erect which allows them to trap air. In this way, heat is trapped inside the hairs which raise the body temperature during cold (an example of homeostasis).
Blood capillaries are also present inside the dermis and they also play a very important part in maintaining the body temperature.
When the arterioles dilate (during hotter conditions), more blood flows through them (to lose some heat to cool the body). However, when they contract (during cold), less blood flows through them.
Apart, the sebaceous gland in the skin is responsible for secreting sebum (an oily substance) which keeps the hair smooth, soft and even lubricates them.
It also prevents the entry of pathogens (such as bacteria) to the body. The nerve endings in the skin also play an important role in detecting the changes in temperature in the body.
Lastly, the sweat gland is responsible for producing sweat. When the temperature of the body rises, heat from the body is lost through sweat.
However, less sweat is produced during the cold in order to maintain heat during cold. The actions of the body during hot and cold are summarised below.
During summers (hotter conditions):
- Blood vessels dilate (vasodilation)
- Sweat gland produces more sweat
- The metabolic rate decreases
- Heat is lost through urine, faeces and expired (exhaled) air
During winters (colder conditions):
- Blood vessels constrict (lesser blood flows to prevent heat loss)
- Shivering occurs to increase body temperature
- The metabolic rate increases the generate more heat
- The sweat glands become less active (to prevent heat loss)
Conclusion:
With this, our article about homeostasis has come to an end. I hope that all your questions have been answered through this article.
The topics covered in this article are listed below for your reference:
- What is meant by homeostasis?
- What is negative feedback?
- Osmoregulation (maintenance of water potential)
- Maintainance of blood glucose concentration
- Diabetes
- Skin
- Thermoregulation (maintenance of temperature)
Thank you very much for reading till the end and stay tuned for more.


Comments
Post a Comment